Chapter 1. Heredity and Evolution
1. Heredity and Evolution
Introduction:
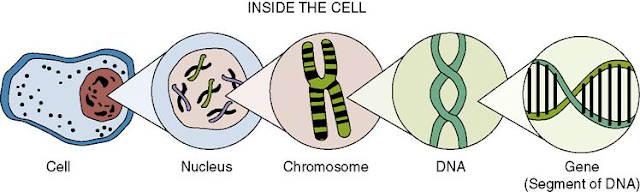
- Basic unit of life is cell.
- Controlling center of cell is nucleus.
- Inside nucleus there are chromosomes.
- Chromosomes are made up of DNA.
- Segment of DNA is called as gene.
✱ Heredity and Hereditary Changes:
Heredity: Transfer of characters from one generation to another via genes.
- Johann Gregor Mendel - Father of modern genetics.
- Hugo de Vries - Mutation Theory (1901).
- Walter and Sutton - Observed paired chromosomes in cells of grasshopper.
- Ostwald Avery, Maclyn McCarthy and Colin MacLeod - Except viruses, all living organisms have DNA as genetic material (1944).
- Francois Jacob and Jack Monad - Proposed a model for process of protein synthesis.
- Diagnosis, treatment and prevention of hereditary disorders.
- Production of hybrid varieties of animals and plants.
- In industrial processes in which microbes are used.
✱ Structure of DNA (Deoxyribo Nucleic Acid)
- Chromosomes are made up of DNA.
- Chromosomes are always in pairs.
- Human cell have 46 chromosomes.
- 4 types of nitrogenous bases are present in DNA: Adenine (A), Guanine (G), Cytosine (C), Thymine (T).
- Adenine only pairs with Thymine (A = T)
- Guanine only pairs with Cytosine (C ≡ G)
- DNA is a twisted structure.
✱ Structure of RNA (Ribonucleic Acid)
- RNA is single stranded.
- 4 types of nitrogenous bases are present in RNA: Adenine (A), Guanine (G), Cytosine (C), Uracil (U).
- There are 3 types of RNA present inside the cell: mRNA (Messenger RNA), rRNA (Ribosomal RNA) and tRNA (Transfer RNA).
✱ Transcription, translation and translocation:
- Information about protein synthesis is stored in DNA.
- Proteins are synthesized by DNA through RNA.
This is called " Central Dogma"
- mRNA is produced as per the sequence of nucleotides on DNA.
- Only one of the two strands of DNA is used in this process.
- Sequence of nucleotides on mRNA is complementary to the DNA strand. Process of RNA synthesis is called transcription.
- Dr Har Gobind Khorana - Important contribution in the discovery of triplet codon.
- Each mRNA is made up of thousands of triplet codon.
- mRNA is used to make proteins. Proteins are made up of amino acids.
- Amino acids are supplied by tRNA. tRNA has anticodons having complementary sequence to the codon on mRNA.
- The process of making proteins using mRNA is known as 'translation'
- The amino acids brought in by tRNA are bonded together by peptide bonds with the help of rRNA.
- Ribosome attach to the mRNA to form proteins. The ribosome keeps on moving from one end of the mRNA to the other end by the distance of one triplet codon. This is called 'translocation'
- Proteins control various functions in body.
- Sometimes sudden changes occur in genes. This is called mutations.
✱ Evolution:
- Evolution is the gradual change occurring in living organisms over a long duration.
- 3.5 billion years ago, life had been non existent on earth.
- Only simple elements present in the ocean on earth.
- Organic and inorganic compounds have been formed from those.
- Proteins and nucleic acids may have formed over the long period from those simple compounds.
- Primitive type of cells may have been formed.
- Number of these cells may have increased at the cost of surrounding chemicals.
- Some differences may have developed among those cells.
- Some may have shown good growth and some may have perished which could not adjust with the surrounding.
- This is the principle of Natural Selection.
- Changes occurred in unicellular organisms from which larger and more complex organisms were formed.
- Duration of all these changes is at most 300 crore years.
- At present crores of species of plants and animals with huge diversity regarding shape and complexity are present on the earth.
✱ Evidences of Evolution:
- Morphological Evidences:
- Morphology means the structure of organism.
- Various similarities can be seen in animals in the above picture, like structure of mouth, position of eyes, structural of nostrils and ear pinnae and thickly distributed hairs on body.
- Various similarities can be seen in plants as well like leaf shape, leaf venation and leaf petiole.
- This indicates that there are some similarities in those groups and hence it proves that their origin must be same and must have common ancestors.
2. Anatomical Evidences:
- If you carefully observe the pictures, there doesn’t seem any superficial similarity between human hand, foreleg of ox, flipper of whale and patagium of bat.
- Similarly, use of each of those structures is different in respective animals.
- However, there is similarity in structure of bones and joints in organs of each of those animals.
- This similarity indicates that those animals may have common ancestor.
3. Vestigial Organs:
- Some structures of organs under different situations may become useless.
- These existing organs undergo gradual changes.
- They began to generate under such conditions.
- It takes thousands of years for a structure to disappear.
- Appendix, which is useless to human, is useful and fully functional organ in ruminants.
- Muscles of ear pinna, which are useless to human, are useful in other mammals for movement of ear pinna.
- Tail bone (Coccyx), body hair and wisdom teeth are some other examples of vestigial organs.
- Degenerated or underdeveloped useless organs of organisms are called as vestigial organs.
4. Paleontological Evidence:
- Large number of organisms get buried due to disasters like volcanic eruption, earthquakes, floods etc.
- Remnants of such organisms remain preserved underground. These are called fossils.
- The time passed since the death of a plant or animal can be calculated using a procedure known as 'Carbon Dating'
- Carbon isotopes C12 and C14 are present inside animals and plants. C14 is radioactive and C12 is non-radioactive. The ration of C14 and C12 remain constant till the animal is alive.
- Once the animal is dead the ratio of C14 and C12 changes continuously. This ratio can be used to determine the time passed since the death of animal of plant.
5. Connecting Links:
- Some animals show characters of two different groups, hence they are called as connecting links.
- Peripatus is an animal which shoes characteristics of annelida and arthropoda. Characteristics of annelida are segmented body, thin cuticle and parapodia like organs. characteristics of arthropoda are tracheal respiration and open circulatory system. Peripatus show characteristics of both these gropus and hence it is a connecting link between annelida and arthropoda.
- Another example is duck-billed platypus which is a connecting link between reptiles and mammals as it shows characteristics of both these groups. One characteristic of reptile is they lay eggs. Characteristic of mammals is present of mammary glands and presence of hairs on body. Duck-billed platypus show characteristics of both these groups and hence it is a connecting link between reptile and mammals. This example indicates that mammals have evolved from reptiles.
6. Embryological Evidence:
- Comparative study of embryonic developmental stages of various vertebrates given in the picture shows that all embryos show extreme similarities during initial stages and those similarities decrease gradually.
- Similarities in initial stages indicate the common origin of all these animals.
✱ Darwin's Theory of Natural Selection:
- Darwin says that all the organisms reproduce prolifically (in large quantities)
- All the organisms compete with each other in a life threatening manner
- Only those organisms sustain which show the modifications essential for winning the competition.
- Sustaining and selected organisms can perform reproduction and thereby give rise to the new species with their own specific characters.
- Darwin's theory of natural selection was widely accepted for a long duration.
- Some objections were raised against the theory:
- Natural selection is not the only factor responsible for evolution.
- Darwin did not mention any explanation about useful and useless modification.
- There is no explanation about slow and abrupt changes.
✱ Lamarckism:
- Given by Jean-Baptiste Lamarck.
- Due to activeness or laziness of organisms, some morphological changes occur in organisms which are responsible for evolution.
- He called this concept as principle of 'use and disuse of organs'
- Neck of giraffe has become too long due to extending their neck for several generations.
- Shoulders of ironsmith have become very strong due to frequent hammering movements.
- Wings of birds like ostrich and emu have become weak due to no use.
- Legs of birds like swan and duck have become useful for swimming due to living in water.
- Snakes have lost their legs by modification in their body for burrowing habit.
- All these examples are of 'acquired characters' and are transferred from one generation to another generation.
- This is called as "Theory of inheritance of acquired characters" or "Lamarckism"
- This theory was widely accepted but transfer of characters was rejected.
- It had been verified many times that modifications brought in us are not transferred to next generation and hence Lamarck's theory was disproved.
✱ Speciation:
- Formation of new species of plant and animals is the effect of evolution.
- Species is the group of organisms that can produce fertile individuals through natural reproduction.
- Each species grow in natural geographical condition.
- Their food, habitat, reproductive ability and period is different.
- Genetic variation is responsible for formation of new species from earlier one.
- Geographical and reproductive changes are also responsible.
- Geographical or reproductive isolation also leads to speciation.
✱ Human Evolution:
- 7 crore years ago: Last dinosaurs disappeared.
- From lemur like ancestors, monkey like animals evolved.
- 4 crore years ago in Africa: Tail of these monkey like animals disappeared. Enlargement in brain and their hands were also improved.
- These ape-like animals reached South and North East Asia and evolved into gibbon and orangutan.
- Some remained in Africa and from them gorilla and chimpanzee evolved about 2.5 crore years ago.
- 2 crore years ago: Some species of apes evolved in a different way. Forest started to decline. They started to live on land.
- Their pelvic girdle developed in such a way that they started to stand in erect posture. Their hands became available for use.
- 1 crore years ago: First record of human-like animal is with us in the form of "Ramapithecus" ape from North India and East Africa.
- 40 lakh years ago: This ape grow up in size and become more intelligent. Ape of South Africa evolved.
- 20 lakh years ago: Skilled human developed. Morphology appeared to be like the member of genus Homo.
- 15 lakh years ago: Human walking with erect posture. It may have existed in China and Indonesia of Asian continent.
- Evolution of upright man continued in the direction of developing its brain for the period of about 1 lakh years and meanwhile it discovered fire.
- 1.5 to 1 lakh years ago: First example of wise man - Neanderthal.
- 50 thousand years ago: Cro-Magnon man evolved and afterwards this evolution had been faster than the earlier.
- 10 thousand years ago: Agriculture started. Man started to rear cattle herds and establish the cities.
- 5,000 years ago: Writing was invented and thus history had been started.
- 400 years ago: Modern science emerged.
- 200 years ago: Industrial society established.
References:
- Inside the Cell (Image): https://www.civilsdaily.com/biotechnology-basics-of-cell-nucleus-chromosomes-dna-genes-etc/
- Structure of DNA (Image): https://study.com/academy/lesson/nitrogenous-base-definition-pairs-quiz.html
- Structure of RNA (Image): https://www.yourgenome.org/theme/what-is-rna/
- mRNA, rRNA and tRNA (Image): https://ib.bioninja.com.au/types-of-rna/
- Complementarity between DNA and mRNA (Image): https://slideplayer.com/slide/7831640/
- Triplet Codons (Image): https://biologyreader.com/genetic-codons.html
- Complementary sequence between codon and anticodon (Image): https://www.quora.com/Since-the-anticodon-of-every-tRNA-is-fixed-does-every-tRNA-go-and-check-which-codon-is-next-in-the-sequence-and-see-if-their-complementary-codon-is-next-in-the-sequence-or-not
- Peripatus (Image): https://predatorfreenz.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/05/There-are-around-200-species-of-peripatus-worldwide.-In-New-Zealand-there-may-be-up-to-30-species.-Image-credit_-Sara-Smerdon.jpg
- Duck-billed Platypus with eggs (Image): https://i.ytimg.com/vi/z0-qFKpktkA/maxresdefault.jpg
- Lungfish (Image): https://cdn.britannica.com/21/2221-004-E610423C/African-lungfish.jpg

















Comments
Post a Comment