Chapter 2. Life Processes in Living Organisms - Part I
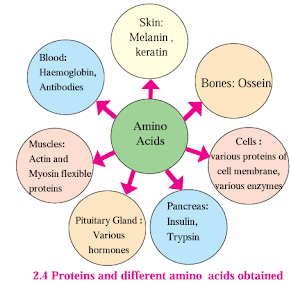
2. Life Processes in Living Organisms - Part I ✱ Energy from different food components: Various organ-systems perform their functions in human body. Digestive system, respiratory system, circulatory system, excretory system, nervous system. All these system require energy. Energy is obtained from food. Food contains nutrients like carbohydrates, proteins, fats. For obtaining energy only nutrients are not sufficient, but oxygen is also necessary. All these foodstuff and oxygen are transported up to the cell via a circulatory system. 1. Carbohydrates: Sources of carbohydrates: Milk, fruits, jaggary, cane sugar, vegetables, potatoes, sweet meats and cereals like wheat, maize, ragi, jowar, millet, rice etc. 1 gm of carbohydrate = 4 Kcal of energy (Kcal = Kilocalorie) 2. Proteins: Sources of proteins: Pulses, egg, fish, chicken, mutton. Animal proteins are called 'first class' protein. 1 gm protein = 4 Kcal of energy. Proteins are formed by amino acids. Hence on digestion, prote...