Simple Epithelium Tissue
The simple epithelium tissue consist of a single layer of cells. An epithelium tissue consist of cells that form membranes, which cover and line the body surfaces and glands. The simple epithelium tissue can be further classified into 4 types:
- Simple Squamous Epithelium
- Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
- Simple Columnar Epithelium
- Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
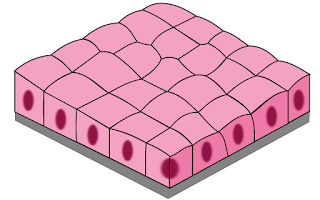
- Simple Squamous Epithelium:
Description: Single layer of cells with a centrally located nucleus. The cells are flat.
Location: Lines the heart, blood vessels, bowman's capsule, air sacs of lungs and inner surface of the eardrum (tympanic membrane).
Function: Filtration, diffusion and osmosis.
Simple Squamous Epithelium
- Simple Cuboidal Epithelium:
Description: Single layer of cells with a centrally located nucleus. The cells are cube shaped.
Location: Surface of ovary, anterior surface of eye lens, lines the kidney tubules, found in the ducts of pancreas.
Function: Secretion and absorption.
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
- Simple Columnar Epithelium:
It is classified into two types non ciliated columnar epithelium and ciliated columnar epithelium.
Non Ciliated Columnar Epithelium:
Description: Single layer of cells with columnar cells (Column-like cells). The nucleus is near to the base. It is modified into two types. Cells containing microvilli and goblet cells. Microvilli are finger like projections of approximately 1 micro-meter, they are present on the apical surface of cells and helps to increase the surface area. Goblet cells are modified columnar epithelial cells which secrete mucous at their apical surface. It serves as a lubricant for the lining of digestive, respiratory, reproductive and urinary tract.
Location: Gallbladder, ducts of many glands, lines the gastrointestinal tract from stomach to anus.
Function: Secretion, absorption and protection.
Ciliated Columnar Epithelium:
Description: Single layer of cells with nucleus at the base. The cells are column-like. Cilia is present at the apical surface. Cilia are about 4-7 micro-meter in length.
Location: Respiratory tract, Fallopian tubes, ventricles of brain.
Function: Moves substances by ciliary action.
- Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium:
Description: Nucleus of the cells are at different levels, not all cells reach the apical surface.
Location: airways of upper respiratory tract
Function: Secretion and movement by ciliary action.
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium






Comments
Post a Comment